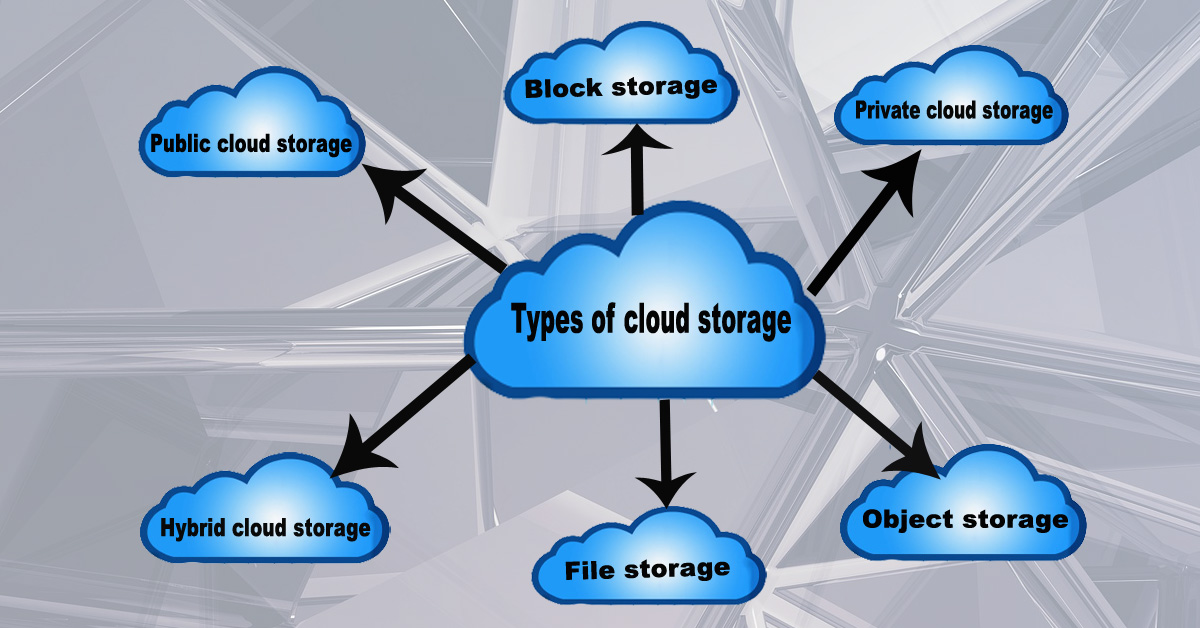
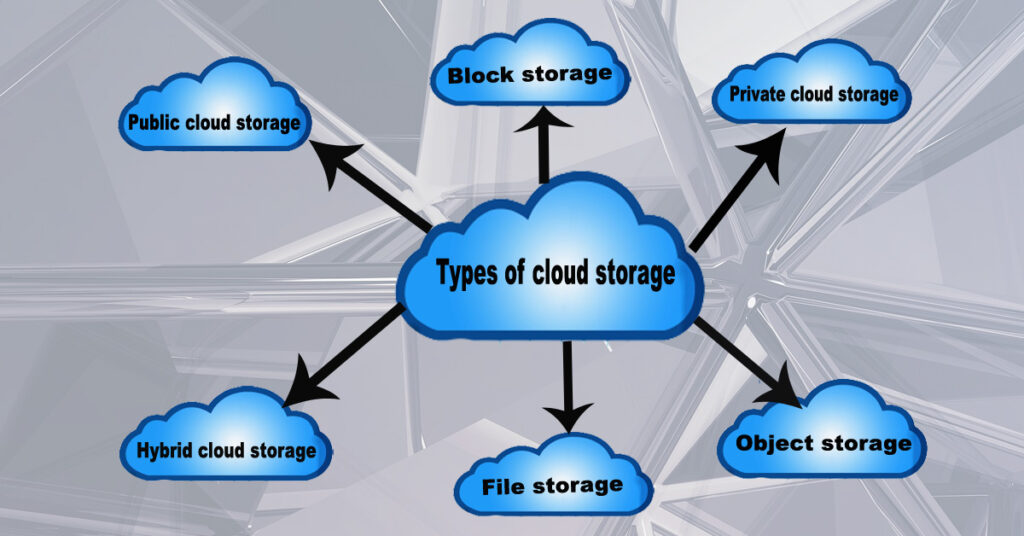
Types of cloud storage
There are several types of cloud storage that are commonly used, including: Public cloud storage, Private cloud storage, Hybrid cloud storage, Object storage, Block storage, File storage.
Cloud storage is a type of data storage where digital data is stored remotely on servers that are owned and managed by a third-party provider. The data is accessible over the internet, which allows users to store and access their files from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud storage is typically used to store and backup data such as documents, photos, videos, music, and other digital files. Some popular cloud storage providers include Google Drive, Dropbox, Microsoft OneDrive, and Amazon S3.
Types of Cloud Storage:
Public cloud storage:
Public cloud storage has transformed the way we store and manage data. It has become an essential part of modern businesses and individuals who rely on data for day-to-day operations. In this essay, we will explore the concept of public cloud storage, its benefits, challenges, and security concerns.
Public cloud storage refers to a service that offers users remote access to a shared pool of storage space. The service provider is responsible for managing and maintaining the infrastructure, including the hardware, software, and security. The storage is available on-demand and is accessed over the internet through a web interface, API, or client software. Examples of popular public cloud storage providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Storage, and Microsoft Azure.
One of the primary benefits of public cloud storage is its scalability. Businesses and individuals can store as much data as they need, and the provider will allocate more storage as required. This means that users do not have to worry about running out of storage space and can focus on their core business. Additionally, public cloud storage is cost-effective because users only pay for the storage they use.
Another advantage of public cloud storage is its accessibility. Users can access their data from anywhere in the world, as long as they have an internet connection. This is particularly useful for remote teams or individuals who need to collaborate on projects or access their files on the go. Public cloud storage also offers automatic backup and recovery, reducing the risk of data loss due to hardware failure or natural disasters.
Despite the benefits, public cloud storage also comes with its own set of challenges. One of the main concerns is security. Storing sensitive data on a third-party server raises questions about who has access to the data and how it is secured. Providers have to implement strict security measures to protect the data, but there is always the risk of data breaches, which can result in reputational and financial damage to businesses.
Another challenge is the lack of control over the infrastructure. Users have limited control over the hardware, software, and security of the public cloud storage service. This can be problematic if the user requires specific software or hardware that is not available in the public cloud environment. Additionally, if the provider experiences downtime, users may not be able to access their data, which can result in a loss of productivity and revenue.
To address these challenges, public cloud storage providers offer different levels of service and support. Users can choose between different service levels, depending on their needs and budget. Providers also offer tools and APIs that allow users to customize and automate their workflows, making it easier to manage their data.
In conclusion, public cloud storage is a popular and essential service that has transformed the way we store and manage data. Its benefits, including scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, make it an attractive option for businesses and individuals. However, its challenges, such as security and lack of control, need to be carefully considered before adopting a public cloud storage solution. By working closely with a reputable provider and implementing best practices for data management and security, businesses and individuals can leverage public cloud storage to their advantage.
Private cloud storage:
In recent years, private cloud storage has become increasingly popular as a data storage solution for businesses and individuals alike. Private cloud storage is a type of cloud computing that provides data storage and management services over the internet, but with the added security and control of a private network. In this essay, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of private cloud storage, its applications, and how it compares to other types of data storage.
Advantages of Private Cloud Storage:
One of the primary advantages of private cloud storage is the added security and control it provides over data. Because it is hosted on a private network, private cloud storage is not accessible to the public, which means that the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches is reduced. Private cloud storage also allows for greater control over data, as users can set their own security protocols, access controls, and backup and recovery processes.
Another advantage of private cloud storage is its scalability. Private cloud storage can be scaled up or down as needed, which means that businesses can easily add or remove storage capacity based on their changing needs. This makes private cloud storage a cost-effective solution for businesses that need to store large amounts of data but don’t want to invest in expensive hardware or software.
Applications of Private Cloud Storage:
Private cloud storage is used in a variety of applications, including data backup and recovery, file sharing, and hosting web applications. In the case of data backup and recovery, private cloud storage provides a reliable and secure way to store data offsite, which reduces the risk of data loss due to natural disasters, hardware failures, or other unforeseen events.
In terms of file sharing, private cloud storage allows users to share files securely with other users within the organization or with external partners. This can be especially useful for businesses that need to share large files or collaborate on projects across multiple locations.
Finally, private cloud storage can be used to host web applications, which allows businesses to take advantage of the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing without sacrificing security or control over their data.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud Storage:
One of the main disadvantages of private cloud storage is the cost. Private cloud storage requires a significant investment in hardware, software, and IT resources, which can make it a more expensive solution than other types of data storage, such as public cloud storage or on-premise storage.
Another disadvantage of private cloud storage is the complexity of its setup and maintenance. Private cloud storage requires a high level of technical expertise to set up and manage, which can be a barrier to entry for small businesses or individuals who may not have the necessary resources or expertise.
How Private Cloud Storage Compares to Other Types of Data Storage:
When compared to other types of data storage, such as public cloud storage or on-premise storage, private cloud storage offers a unique set of advantages and disadvantages.
Public cloud storage is a popular option for businesses and individuals because it is cost-effective and easy to use. However, public cloud storage can also be less secure and less customizable than private cloud storage, which can be a concern for businesses that need to store sensitive or confidential data.
On-premise storage, on the other hand, offers the highest level of control and security over data, but it can also be expensive and require a significant investment in hardware and IT resources.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, private cloud storage offers a number of advantages for businesses and individuals who need a secure and scalable data storage solution. While it may be more expensive and complex to set up and maintain than other types of data storage, the added security and control it provides can make it a worthwhile investment for businesses that need to store sensitive or confidential data. As cloud computing continues to evolve, private cloud storage will likely continue to be an important part of the data storage landscape for years to come.
Hybrid cloud storage:
Introduction:
Hybrid cloud storage is a new technology in the cloud computing world that enables organizations to combine public and private cloud storage systems for data storage and management. Hybrid cloud storage has become an increasingly popular alternative for many organizations looking to take advantage of the benefits of cloud storage while maintaining the security of private data. This essay aims to provide an overview of hybrid cloud storage and how it works, benefits, challenges, and real-world examples of hybrid cloud storage.
What is Hybrid Cloud Storage?
Hybrid cloud storage is a model that enables organizations to use public cloud storage systems, private cloud storage systems, and on-premise storage solutions. This model is designed to help organizations to balance their storage needs in terms of data protection, security, and cost-effectiveness. The hybrid cloud storage system combines the benefits of both public and private cloud storage systems. The public cloud is ideal for storing less sensitive data and is cost-effective, while the private cloud provides a more secure platform for storing sensitive and mission-critical data.
How Does Hybrid Cloud Storage Work?
Hybrid cloud storage systems work by providing a platform where organizations can store data on both public and private clouds. The storage system uses a combination of technologies that enable data to move between public and private clouds seamlessly. In most cases, hybrid cloud storage systems use a common interface that makes it easy for organizations to manage data across the two platforms. The data stored on the public cloud can be accessed via the internet while data stored on the private cloud can only be accessed within the organization’s internal network.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Storage:
- Cost-effectiveness: Hybrid cloud storage enables organizations to reduce their storage costs significantly. With a hybrid cloud storage system, organizations can take advantage of the cost-effectiveness of public cloud storage while still enjoying the benefits of private cloud storage.
- Data security: Hybrid cloud storage provides organizations with the flexibility to store sensitive and confidential data on their private cloud. This is ideal for organizations that deal with sensitive data and need to maintain the highest level of security.
- Scalability: Hybrid cloud storage is highly scalable and can accommodate organizations of any size. With a hybrid cloud storage system, organizations can scale their storage needs up or down, depending on their requirements.
- Backup and recovery: Hybrid cloud storage provides organizations with a robust backup and recovery system. Data is replicated across both public and private clouds, ensuring that data is always available, even in the event of a disaster.
Challenges of Hybrid Cloud Storage:
- Integration: One of the major challenges of hybrid cloud storage is integration. Hybrid cloud storage systems require organizations to integrate different cloud platforms, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Security: While hybrid cloud storage provides an ideal platform for storing sensitive data, it also poses some security challenges. Organizations need to ensure that data stored on the public cloud is secure, and only authorized personnel can access it.
- Data management: Managing data across multiple cloud platforms can be challenging. Organizations need to ensure that data is consistent across both platforms and is accessible to authorized personnel.
Real-World Examples of Hybrid Cloud Storage:
- Netflix – Netflix uses a hybrid cloud storage model to store its vast video library. The company stores frequently accessed content in its own data centers, while less frequently accessed content is stored on the public cloud. This enables the company to efficiently manage its storage costs and ensure quick access to its content for its users.
- Coca-Cola – Coca-Cola uses a hybrid cloud storage model to store its massive amounts of data. The company stores critical data, such as financial and customer information, on its own private cloud, while less sensitive data is stored on the public cloud. This helps Coca-Cola manage its storage costs while also ensuring the security of its most sensitive information.
- PwC – PwC, a global professional services firm, uses a hybrid cloud storage model to store its clients’ sensitive data. PwC stores the most sensitive data on its private cloud, while less sensitive data is stored on the public cloud. This enables PwC to offer its clients a high level of security and confidentiality, while also providing the flexibility and scalability of the public cloud.
- NASA – NASA uses a hybrid cloud storage model to manage its vast amounts of data. NASA stores critical data on its own private cloud, while less critical data is stored on the public cloud. This enables the agency to efficiently manage its storage costs while ensuring the security and accessibility of its critical data.
- The University of Notre Dame – The University of Notre Dame uses a hybrid cloud storage model to store its research data. The university stores sensitive research data on its private cloud, while less sensitive data is stored on the public cloud. This enables the university to manage its storage costs while also ensuring the security and confidentiality of its research data.
- GE Oil & Gas: GE Oil & Gas has adopted hybrid cloud storage to store its vast data on oil and gas exploration. The company uses a combination of public and private clouds to store its data. This has enabled the company to reduce its storage costs significantly while still maintaining the highest level of data security.
Object storage:
Object storage is a data storage architecture that manages and organizes data as objects, rather than files or blocks. These objects are self-contained and include the data itself, metadata, and a unique identifier that distinguishes them from one another. Object storage is an alternative to traditional file and block storage systems that are widely used today.
Object storage systems are designed to store large amounts of unstructured data, such as images, videos, audio files, and documents. They are also capable of storing structured data, but are not optimized for this use case. Object storage is ideal for organizations that require scalable, flexible, and cost-effective storage solutions.
Object storage is a distributed storage system that is designed to work across multiple servers or data centers. This means that objects can be stored in multiple locations, making them highly available and fault-tolerant. The data is typically accessed through a RESTful API, which allows for easy integration with applications and services.
Object storage systems are typically built using commodity hardware, which makes them more cost-effective than traditional storage systems. Additionally, they are designed to scale horizontally, which means that additional storage capacity can be added by simply adding more servers to the system.
One of the key benefits of object storage is its ability to store large amounts of data without the need for a hierarchical file system. This means that objects can be accessed and managed in a more flexible manner, which is particularly useful for organizations that deal with a large amount of unstructured data.
Another advantage of object storage is its ability to provide better data durability and availability. Because objects are replicated across multiple locations, they are less vulnerable to data loss or downtime caused by hardware failure, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events.
Object storage is also highly scalable, which means that it can accommodate growth in data volumes and user demands. This scalability is achieved through the use of distributed storage architectures, which enable data to be stored across multiple nodes or servers.
Finally, object storage is highly efficient when it comes to data management and storage. Because objects are self-contained, they can be easily moved or deleted without affecting other data. Additionally, object storage systems use data deduplication and compression to reduce storage requirements and optimize performance.
In conclusion, object storage is an innovative storage architecture that provides a number of advantages over traditional file and block storage systems. It is ideal for organizations that need to store large amounts of unstructured data in a scalable, flexible, and cost-effective manner. With the growing demand for data storage, object storage is becoming an increasingly popular solution for businesses of all sizes.
Block storage:
Block storage is a type of data storage that stores data in the form of fixed-size blocks or chunks. Each block has a unique address and can be accessed independently of other blocks in the storage. Block storage is commonly used in enterprise environments and cloud computing, where high-performance storage is required for running applications and storing large amounts of data.
Block storage is different from file storage and object storage, which are other types of data storage. File storage stores data in the form of files, while object storage stores data in the form of objects with metadata. Block storage, on the other hand, stores data in the form of blocks with no metadata. This makes block storage faster and more efficient than file storage and object storage, as it allows for direct access to data without the need for metadata lookup.
Block storage is commonly used in enterprise environments for running databases, virtual machines, and other applications that require high-performance storage. This is because block storage provides low-latency access to data and allows for high IOPS (input/output operations per second). In addition, block storage is scalable, allowing enterprises to add storage capacity as needed to meet the demands of their applications.
In cloud computing, block storage is often used as a storage option for virtual machines (VMs) and other cloud-based applications. Cloud providers offer block storage as a service, allowing customers to provision and manage block storage volumes on-demand. This enables customers to easily scale their storage capacity to meet the needs of their applications without having to invest in physical storage hardware.
Block storage is also used in storage area networks (SANs) and network-attached storage (NAS) systems. SANs are used to provide high-performance block-level access to storage resources, while NAS systems provide file-level access to storage resources. In both cases, block storage is used to provide fast and efficient access to data.
One of the advantages of block storage is that it allows for data replication and data mirroring. This means that data can be replicated or mirrored across multiple storage devices, providing redundancy and data protection. In addition, block storage can be configured to provide snapshots, allowing for point-in-time copies of data that can be used for backup and recovery purposes.
There are two types of block storage: direct-attached storage (DAS) and network-attached storage (NAS). DAS is storage that is directly connected to a server or a computer, while NAS is storage that is connected to a network and can be accessed by multiple servers or computers. Both types of block storage have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs of the application.
In conclusion, block storage is an important type of data storage that is used in enterprise environments and cloud computing. It provides fast and efficient access to data, and allows for scalability and redundancy. Block storage is commonly used for running databases, virtual machines, and other applications that require high-performance storage. As the demands for storage continue to grow, block storage will continue to play an important role in meeting the storage needs of enterprises and cloud providers.
File storage:
File cloud storage has become increasingly popular in recent years as the demand for remote access to files and data has grown. With file cloud storage, users can store and access their files and data from anywhere in the world, as long as they have an internet connection. This technology has revolutionized the way we store and manage our data, and has become a key tool for businesses, professionals, and individuals alike. In this essay, we will discuss the basics of file cloud storage, its benefits, and its potential drawbacks.
File cloud storage, as the name suggests, is a service that allows users to store their files and data in the cloud. This means that the data is stored on remote servers, and users can access it from any device that is connected to the internet. Cloud storage services typically require users to create an account, and then upload their files to the cloud. Once the files are uploaded, users can access them using a web interface, mobile app, or desktop client. In addition to providing storage space for files, many cloud storage services also offer additional features such as file sharing, file syncing, and automatic backups.
One of the main benefits of file cloud storage is the flexibility it provides. With cloud storage, users can access their files from anywhere, at any time. This is particularly useful for businesses and professionals who need to work remotely, as it allows them to access their files and data from home, on the road, or from any other location with an internet connection. Additionally, cloud storage services are often scalable, meaning that users can increase their storage capacity as their needs grow. This is much more convenient than having to physically upgrade hardware, and can be done quickly and easily with just a few clicks.
Another benefit of file cloud storage is the added security it provides. With cloud storage, files are stored on remote servers, which are typically more secure than a user’s local device. This is because cloud storage providers typically have better security measures in place, including encryption, firewalls, and other security features. Additionally, many cloud storage services offer advanced security features such as two-factor authentication and password protection to further enhance the security of stored data.
However, there are also potential drawbacks to using file cloud storage. One of the main concerns is the privacy of stored data. While cloud storage providers typically have strong security measures in place, there is always the risk of data breaches or hacks. In addition, some users may be uncomfortable with the idea of storing sensitive or personal data on remote servers, and may prefer to keep their files stored locally. Furthermore, cloud storage services typically require a subscription fee, which can add up over time, particularly for users with large storage needs.
In conclusion, file cloud storage has become an essential tool for businesses, professionals, and individuals who need remote access to their files and data. The benefits of cloud storage, including flexibility, scalability, and added security, make it an attractive option for many users. However, there are also potential drawbacks to consider, including concerns about privacy and ongoing subscription costs. Ultimately, users should carefully consider their storage needs and the level of security and privacy they require before choosing a cloud storage service.
People also ask:
How much does 1TB of cloud storage cost?
The cost of 1TB of cloud storage can vary depending on the cloud storage provider and the specific plan you choose. Here are some examples of pricing for 1TB of cloud storage from popular providers:
- Google One: 1TB of storage costs $9.99 per month or $99.99 per year.
- Dropbox: 1TB of storage costs $9.99 per month or $119.88 per year.
- Microsoft OneDrive: 1TB of storage is included with a Microsoft 365 subscription, which starts at $5 per month or $59.99 per year for personal use. Standalone OneDrive plans start at $1.99 per month for 100GB of storage and go up to $9.99 per month for 6TB of storage.
- iCloud: 1TB of storage costs $9.99 per month.
It’s worth noting that many cloud storage providers offer different storage tiers, so the cost of 1TB may vary depending on the provider and plan you choose. Additionally, some providers may offer discounts for annual subscriptions, so it’s worth exploring different options to find the best deal for your needs.
Is Google giving 1TB free?
However, as of my last update, Google is not offering 1TB of free storage to its users. Google does offer a certain amount of free storage for Google Drive, but it is limited and subject to change at any time. It’s best to check Google’s official website or news outlets for the latest updates on their services and offerings.
How much does 1TB cloud storage cost India?
The cost of 1TB cloud storage in India varies depending on the provider and the specific plan. Some popular cloud storage providers in India and their prices for 1TB of storage are:
- Google Drive: INR 1,300/month or INR 13,000/year
- Microsoft OneDrive: INR 6,299/year (including Microsoft 365 Personal subscription)
- Dropbox: INR 1,799/month or INR 18,000/year
- iCloud: INR 749/month or INR 7,900/year
- Amazon Drive: INR 4,200/year (with Amazon Prime subscription)
It is important to note that these prices may be subject to change and may also vary depending on any ongoing promotions or discounts.
How do I get 100GB cloud free?
I don’t have personal preferences or can access to your personal information. However, some cloud services offer 100GB of storage for free. Here are some options:
- Google Drive: Google Drive offers 15GB of free storage, but you can earn an additional 100GB by completing security checks.
- Microsoft OneDrive: Microsoft OneDrive offers 5GB of free storage, but you can earn an additional 100GB by subscribing to Microsoft 365.
- Dropbox: Dropbox offers 2GB of free storage, but you can earn up to 16GB of additional storage by completing certain tasks and referrals.
- Box: Box offers 10GB of free storage, but you can earn an additional 100GB by signing up for a personal pro account.
Note that these offers may vary based on location and time, so be sure to check the terms and conditions of each service.
Which cloud storage is free unlimited?
There is no cloud storage that is completely free and unlimited. While some cloud storage services offer a large amount of storage space for free, they typically have a limit to the amount of storage available or restrict certain features. Additionally, some cloud storage services may offer unlimited storage, but only with a paid subscription. It is important to review the terms and conditions and limitations of any cloud storage service before using it.
What happens if cloud storage is full?
If the cloud storage is full, users will no longer be able to upload new files to the account. They may receive an error message indicating that the storage capacity has been exceeded. In some cases, the cloud storage service may automatically delete older files or ask the user to upgrade to a higher storage plan. Users can also manually delete unnecessary files to free up space. If no action is taken, the user may lose access to their data or experience syncing issues.